Hess's Law
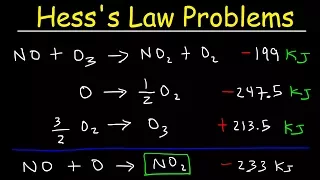
Feb 22, 2020so one way to find the enthalpy change for an equation uses what is known as Hessa's law and the way you use Hessa's law is not that different from what you commonly do in algebra, say for example that you have x + y = 36 and you get another equation equal we have y equal Z + x at the beginning of algebra, you know they taught you how to add equations, in this case you see that the X's are on opposite sides, so they disappear, so when the sums you get 2 y = z + 36 Hess's law does the same kind of thing, but instead of working with algebra equations we use that trick with chemical equations like, for example, you can take these two equations and if you add them like the Hess's law says that when you add two equations together as we did here, the change in entropy for that reaction is the sum of the change in y for equations that were added many times, although when they give you the equation, sometimes they don't give you where you can add them automatically. add them up well, for example, well, a typical Hess's law problem might be stated like this, where you try to find the enthalpy change of this equation and they give you these three equations here now if you just try to add them together. like we did a minute ago, they won't come close to what they're asking for, so a lot of times you have to modify the equation to get them to add correctly, but when you modify the equation you have to modify it. the eny also changes, so for example, if you look at this first equation, here in this equation hydrogen fluoride is shown and if you look, this is the only place where we see hydrogen fluoride for these three given equations, so whatever we do with hydrogen fluoride or Whatever we do in this equation, it's better to set it up where we have the proper coefficient and HF is on the right side of the equation, so if you look, it's on the right side because it's a product here, it's a product in the equation we want, but you only have two in the given equation and we need four, so we can solve it by multiplying this equation by two.
We are now changing the hydrogen and Florine coefficients, but since we are dealing with HF, I hope this resolves them. and you'll see later they do, but one thing about working with Hessa's Law, whatever you do with the equation, you'll have to do the same thing with your enthalpy change: we're doubling the coefficient, so we got twice as much. Delta H look at the second equation again, try to focus on a substance that you only see in this equation, when you compare it to the equation you want, so in this case we want to focus on c2h4, better known as ethylene. so you have an ethylene on the right, but in the equation we want we have one on the left, so we're going to have to reverse this equation so that when you reverse the equation you actually have to reverse the sign, which means plus 52 becomes - 52 and for this last equation we want to focus on cf4 because carbon is not even in the equation we want.
Florine is actually in a couple of places, so it could be a pain trying to fix Florine, so again, whatever we do for cf4 and this or whatever we do with this equation, we have to fix it where cf4 is in the right place with the right coefficient. These other two will hopefully resolve themselves, so here we have one on the reactant side but we want two on the product side, so we're going to have to multiply it by two and we're going to have to turn it around to put it in the product side of the equation, so we have to take our total change, we have to multiply it. times two and we're going to have to reverse the sign, so when we look at our modified equations and there's our first modified equation where now the coefficients have been multiplied by two, even though I left a four, there we go and we go ahead and multiply the Delta H, we flip this equation and again we flip the sign and for our last equation we had to flip it and double it, so again we flip the sign and double it so that when you add these three equations together we notice that the things that were not part of the overall equation or the things we didn't want in the overall equation our hydrogens those carbons cancel out because they are on opposite sides of our Arrow so that leaves you with 1 C2 H4 plus 6 lines see the Florin solved itself it gives you two cf4 and four HFS again, that's the equation we want and as Hess's law says, again, when you add the equations, the nth will be changed for this.
This reaction you got by adding the equations will be the sum of the changes in y for each equation you added.
If you have any copyright issue, please Contact